Esta web utiliza cookies para que podamos ofrecerte la mejor experiencia de usuario posible. La información de las cookies se almacena en tu navegador y realiza funciones tales como reconocerte cuando vuelves a nuestra web o ayudar a nuestro equipo a comprender qué secciones de la web encuentras más interesantes y útiles.
Blog
Hyperscaler Data Centers and the Importance of Three-Phase PDUs
Today's data centers are experiencing increasing demand for energy consumption, driven by servers that are constantly undergoing consolidation and virtualization.
This trend that started a few years ago and is here to stay. The main contributors to this trend are the Internet of things (IoT), the cloud and new 5G systems, which are pushing energy demands even further than previously imagined. The result is a
increased demand for computing and storage capabilities.
Energy consumption per rack has almost tripled in recent years. A few years ago, it was possible to install 10 high-power servers in an IT rack and achieve a maximum power load of 6
7kW.
Today, new IT limits see more blade servers or many more 1RU servers in the same rack, consuming up to 20 kW per rack.
Single-phase systems distribute current through two wires: a live (active) wire and a neutral wire. The alternating current sine wave crosses the zero point at regular intervals. These
Single-phase systems are frequently installed in residential environments that require a small
energy consumption.
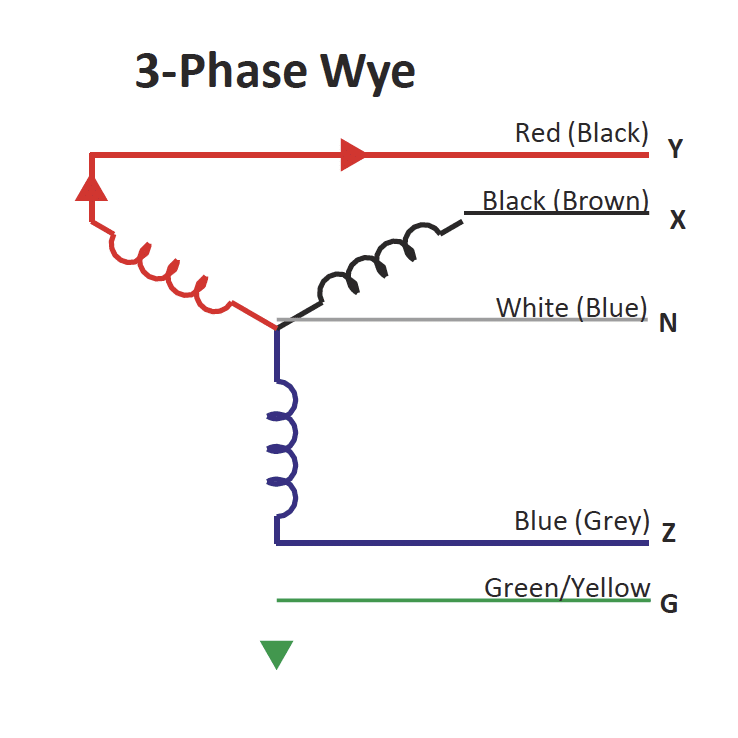
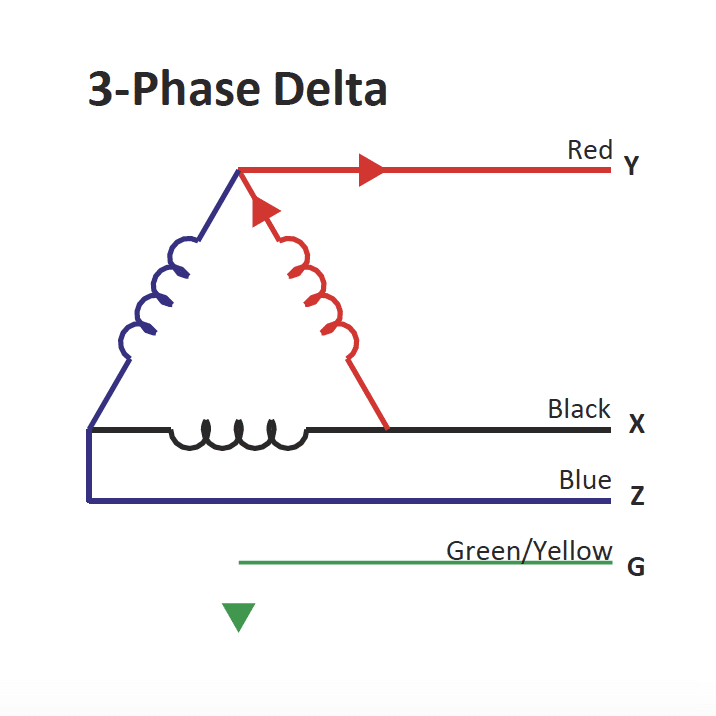
Three-phase systems consist of three sine waves, each positioned at 120 degrees. Each
one (phase) carries a separate wire. Due to the relationship between phases, the current and voltage never drop to
zero. This allows three-phase systems to provide much more power than a system
monophase.
Phase balancing, by connecting loads across all three phases in the PDUs, helps minimize
harmonic currents and the need for large neutral cables. This allows optimal use of
upstream electrical infrastructure capacity, resulting in greater overall efficiency of the
data center and helps minimize costs.
The comparison tables below show the dramatic difference in power capacity
between the single-phase and three-phase PDUs.
| Phase configuration | Voltage/Current | Plug type | Max. power capacity (kW) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Three phase DELTA | 208V 60A | IEC60309 3P+E 60A | 17.2 |
| Three phase WYE | 346-415V 30A | IEC60309 3P+N+E 30A | 16.6 |
| Three phase DELTA | 208V 30A | NEMA L15-30P Twistlock | 8.6 |
| Three phase WYE | 100-120/200-240V 30A | NEMA L21-30P Twistlock | 8.6 |
| Three phase WYE | 200-240/346-415V 30A 3Phase WYE | NEMA L22-30P Twistlock | 16.6 |
| Three phase WYE | 100-120/200-240V 20A 3 Phase WYE | NEMA L21-20P Twistlock | 5.7 |
| Three phase WYE | 200-240/346-415V 20A 3 | NEMA L21-20P Twistlock | 11 |
| single phase | 200-240V 30A 1 Phase | NEMA L6-30P Twistlock | 4.9 |
| single phase | 200-240V 20A 1 Phase | NEMA L6-20P Twistlock | 3.3 |
| single phase | 100-120V 30A 1 Phase | NEMA L5-30P Twistlock | 2.8 |
| single phase | 100-120V 20A 1 Phase | NEMA L5-20P Twistlock | 1.9 |
| Three phase WYE | 380 – 415V 32A | IEC60309 3P+N +E 32A | 22.2 |
| Three phase WYE | 380 – 415V 32A | IEC60309 3P+N +E 16A | 11.1 |
| single phase | 220-250V 32A | IEC60309 1P+N +E 32A | 7.2 |
| single phase | 220-250V 32A | IEC60309 1P+N +E 16A | 3.6 |

















